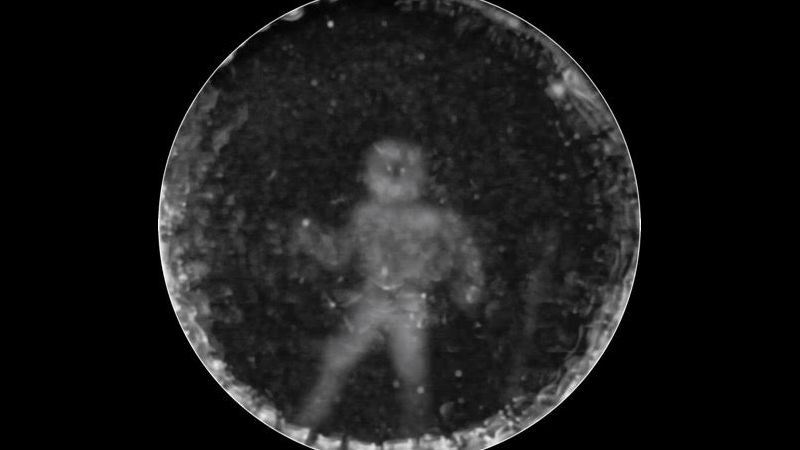
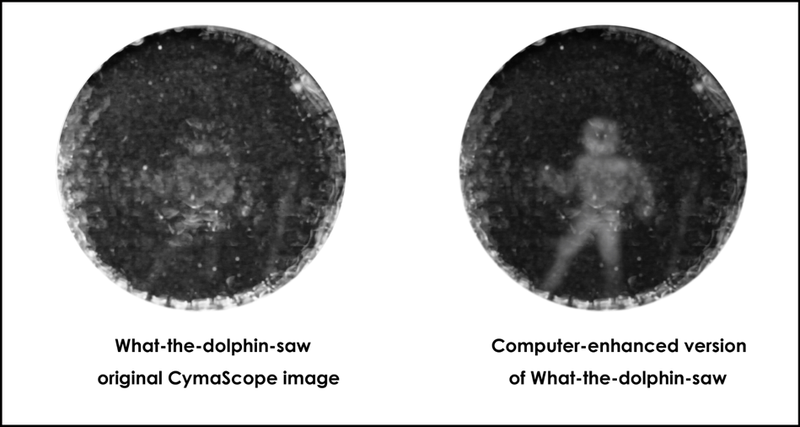
In a world’s first, researchers from the US and UK have created an impression of a submerged human as recorded by a dolphin’s echolocation.
To do it, a team led by Jack Kassewitz of SpeakDolphin.com used an imaging system known as a Cymascope. The system, developed by John Stuart Reid (who also assisted with the project), made it possible to record and isolate dolphin echolocation sounds directed onto specific objects, and then create 2D images from those sounds. A computer then converted those images into 3D, which allowed the researchers to 3D-print robust, real-world models.
“We’ve been working on dolphin communication for more than a decade,” noted Kassewitz in a release. “When we discovered that dolphins not exposed to the echolocation experiment could identify objects from recorded dolphin sounds with 92% accuracy, we began to look for a way for to see what was in those sounds.”

(Credit: SpeakDolphin.com/Cymascope Laboratory)
For the experiment, a female dolphin named Amaya directed her sonar beams at a submerged diver, while a hydrophone captured the ensuing echos. To avoid added “noise,” the diver, Jim McDonough, swam without a breathing apparatus to make sure no bubbles would adversely affect the results. As Amaya scanned McDonough with her high frequency sound beam, the CymaScope imprinted sonic vibrations within the water medium.
In addition to the diver, the researchers also had Amaya direct her sonar at a flowerpot, a cube, and a plastic “+” symbol.
“We were thrilled by the first successful print of a cube by the brilliant team at 3D Systems,” said Kassewitz. “But seeing the 3D print of a human being left us all speechless. For the first time ever, we may be holding in our hands a glimpse into what cetaceans see with sound. Nearly every experiment is bringing us more images with more detail.”
Looking ahead, the team would like to determine if and how dolphins may be sharing these echolocation images as part of an intra-species sono-pictorial language.
[ SpeakDolphin.com | h/t Discovery News ]